Các đối tác tiềm năng trong phép đo nhiệt độ NTC: Điện trở kéo lên và kéo xuống
Oct 15, 2025Khi thiết kế mạch đo nhiệt độ bằng cách sử dụng Nhiệt điện trở NTC, một chi tiết quan trọng thường bị bỏ qua — đối tác thiết yếu của chúng: điện trở kéo lên và kéo xuống. Cùng nhau, chúng tạo thành bộ chia điện áp chuyển đổi sự thay đổi điện trở của NTC theo nhiệt độ thành tín hiệu điện áp có thể đo được cho MCU hoặc mô-đun ADC.
1. Tại sao NTC cần điện trở kéo lên hoặc kéo xuống?
Nhiệt điện trở NTC là thiết bị tương tự chỉ thay đổi điện trở theo nhiệt độ. Tuy nhiên, mạch kỹ thuật số chỉ có thể đọc điện áp chứ không phải điện trở. Vì vậy, một điện trở (kéo lên hoặc kéo xuống) được ghép nối với NTC để tạo ra mạch chia đầu ra điện áp thay đổi tương ứng với nhiệt độ.
Công thức chia điện áp cơ bản là:
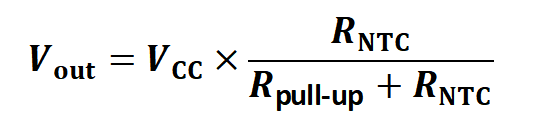
Ở đâu:
Vngoài = điện áp trên NTC (hoặc trên điện trở cố định, tùy thuộc vào cấu hình).
VCC= điện áp cung cấp (ví dụ: 5 V hoặc 3,3 V).
RNTC = điện trở nhiệt điện trở (giảm khi nhiệt độ tăng).
Rkéo lên= điện trở kéo lên hoặc kéo xuống.
2. Kéo lên so với kéo xuống: Kết nối khác nhau, mục đích giống nhau.
|
Kiểu |
Sự liên quan |
Hành vi logic |
Mục đích |
|
Điện trở kéo lên |
Kết nối giữa nút đầu ra VCC và NTC |
Kéo tín hiệu cao khi mở |
Ngăn chặn đầu vào nổi, đảm bảo logic “1” |
|
Điện trở kéo xuống |
Kết nối giữa GND và nút đầu ra NTC |
Kéo tín hiệu thấp khi mở |
Ngăn chặn đầu vào nổi, đảm bảo logic “0” |
Chúng đảm bảo mức điện áp ổn định, ngăn chặn nhiễu điện và bảo vệ các IC nhạy cảm khỏi sự tăng đột biến dòng điện.
3. Hiểu mối quan hệ giữa điện áp-nhiệt độ-logic.
Sử dụng công thức chia: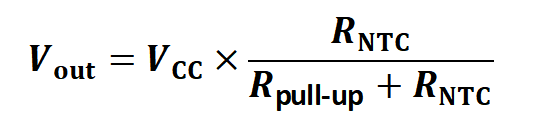
Điều này giúp MCU dễ dàng phát hiện ngưỡng nhiệt độ hoặc liên tục đo nhiệt độ tương tự thông qua đầu vào ADC.
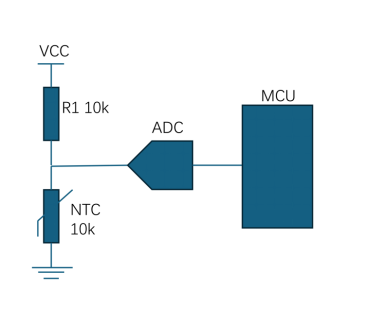
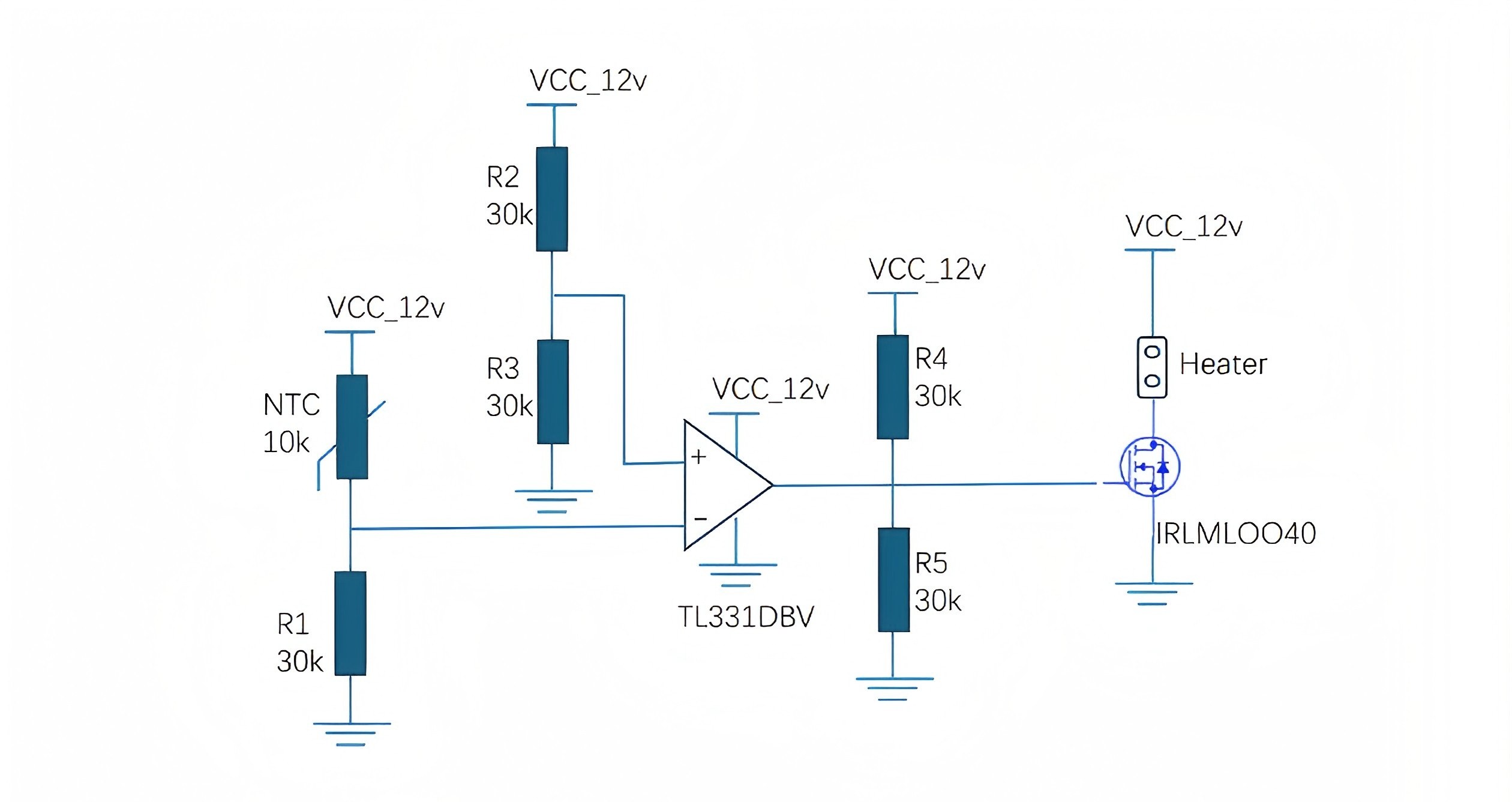
4. Ví dụ về chuyển đổi nhiệt độ sử dụng bộ so sánh.
Đối với điều khiển nhiệt độ đơn giản (không có MCU), mạch so sánh có thể giải thích trực tiếp mức điện áp NTC:
Khi Vout vượt qua ngưỡng tham chiếu:
Ưu điểm: Chi phí thấp, phản hồi nhanh, không cần MCU — lý tưởng để bảo vệ quá nhiệt trong nguồn điện, bộ sạc hoặc mô-đun công nghiệp.
5. Lựa chọn giá trị điện trở phù hợp.
Việc lựa chọn điện trở phù hợp sẽ đảm bảo sự cân bằng giữa mức tiêu thụ điện năng, độ nhạy và khả năng chống nhiễu.
|
Tham số |
Quá nhỏ |
Quá lớn |
Khuyến khích |
|
Giá trị điện trở |
Dòng điện cao → mất nhiệt và năng lượng |
Tín hiệu yếu → nhiễu, mất ổn định |
4,7 kΩ – 10 kΩ cho kỹ thuật số, tính toán cho mỗi bộ chia cho tương tự |
|
Sự va chạm |
Công suất tĩnh cao |
Phản ứng chậm |
Ổn định, tiếng ồn thấp |
6. Tại sao nên hợp tác với Shiheng Electronics?
Với hơn 20 năm kinh nghiệm sản xuất, Shiheng Electronics cung cấp:
Của chúng tôi Nhiệt điện trở dòng MF52 và cảm biến chính xác được sử dụng rộng rãi trong:

Bạn đang muốn thiết kế mạch cảm biến nhiệt độ đáng tin cậy? Liên hệ Shiheng Electronics ngay hôm nay để được hỗ trợ kỹ thuật chuyên môn và giải pháp NTC tùy chỉnh.
Web: www.ntcshiheng.com;Email:Globalsales@shiheng.com.cn.